The Age of AI
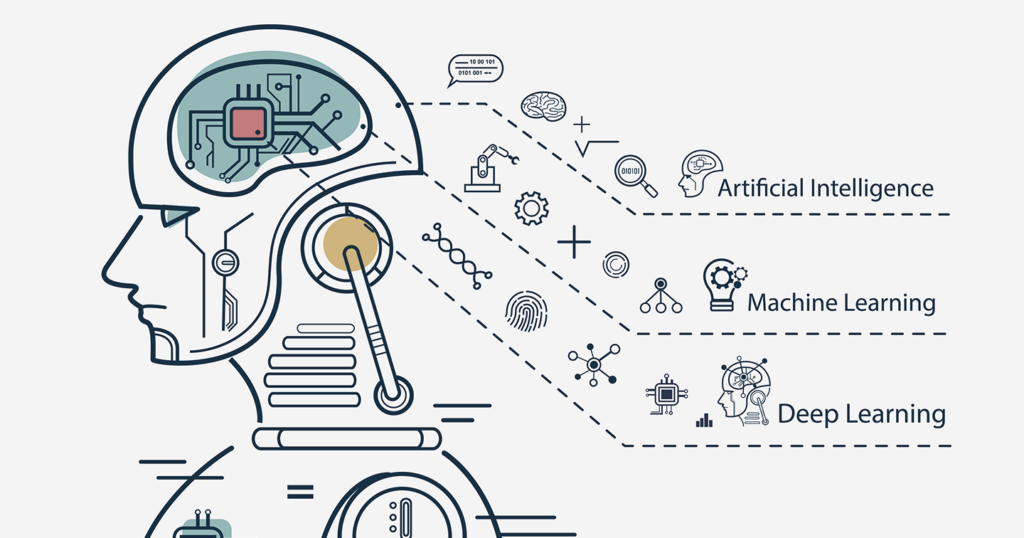
Artificial intelligence allows machines to model, and even improve upon, the capabilities of the human mind. From the development of self-driving cars to the
proliferation of smart assistants like Siri and Alexa, AI is a growing part of everyday life. As a result, many tech companies across various industries are investing in artificially intelligent technologies.
A reactive machine follows the most basic of AI principles and, as its name implies, is capable of only using its intelligence to perceive and react to the world in front of it. A reactive machine cannot store a memory and, as a result, cannot rely on past experiences to inform decision making in real time.
Perceiving the world directly means that reactive machines are designed to complete only a limited number of specialized duties. Intentionally narrowing a reactive machine’s worldview is not any sort of cost-cutting measure, however, and instead means that this type of AI will be more trustworthy and reliable — it will react the same way to the same stimuli every time.
There are several ML models that utilize limited memory AI:
Reinforcement learning, which learns to make better predictions through repeated trial and error.
Recurrent neural networks (RNN), which uses sequential data to take information from prior inputs to influence the current input and output. These are commonly used for ordinal or temporal problems, such as language translation, natural language processing, speech recognition and image captioning. One subset of recurrent neural networks is known as long short term memory (LSTM), which utilizes past data to help predict the next item in a sequence. LTSMs view more recent information as most important when making predictions, and discount data from further in the past while still utilizing it to form conclusions.
Evolutionary generative adversarial networks (E-GAN), which evolve over time, growing to explore slightly modified paths based off of previous experiences with every new decision. This model is constantly in pursuit of a better path and utilizes simulations and statistics, or chance, to predict outcomes throughout its evolutionary mutation cycle.
Transformers, which are networks of nodes that learn how to do a certain task by training on existing data. Instead of having to group elements together, transformers are able to run processes so that every element in the input data pays attention to every other element. Researchers refer to this as “self-attention,” meaning that as soon as it starts training, a transformer can see traces of the entire data set.
“AI is a computer system able to perform tasks that ordinarily require human intelligence ... Many of these artificial intelligence systems are powered by machine learning, some of them are powered by deep learning and some of them are powered by very boring things like rules.”